Have you ever stopped to think about what happens when you bring two vibrant colors like green and blue together? It's a question that pops up a lot, whether you're a painter, a designer, or just someone curious about the world around you. Today, we are going to learn more about the concept of color mixing, so it's quite a fascinating topic to explore.
There's more to color mixing than just pouring two paints into a cup, you know. It's actually a pretty big deal in many different areas, from how your computer screen shows images to how an artist creates a beautiful landscape. Understanding how colors combine, especially green and blue, can really open up a whole new way of looking at things. So, if you are asking yourself ‘what color do green and blue make’, this article can help you get answers.
The specific hue you get when mixing green and blue, it's interesting, will depend a lot on the ratio of blue to green, and also on whether you are working with light or with pigments. It’s essential to understand how color mixing works, whether you’re working with paints, pigments, or even just thinking about the light coming from your phone. Let’s find out more about color, and how these two shades come together.
Table of Contents
- The Magic of Color Mixing: An Introduction
- Green and Blue in Light: Additive Mixing
- Green and Blue with Pigments: Subtractive Mixing
- The Bigger Picture: Color Theory and Perception
- Digital Colors: HTML and Beyond
- Tools to Help You Mix and Match
- Frequently Asked Questions About Green and Blue Mixing
The Magic of Color Mixing: An Introduction
Ever wondered what blue and green make when you mix them together? It’s a question that has sparked curiosity for a long, long time, you know. Color, in a way, is a phenomenon of light, like red, brown, pink, or gray. It's what allows us to tell apart objects that might otherwise look exactly the same. So, understanding how colors behave when they meet is pretty important for anyone working with visuals.
This whole idea of combining colors, it’s actually a really fundamental part of how we create and perceive our visual world. Whether you are painting a picture, designing a website, or even just picking out clothes, the way colors interact plays a big part. Today, we are going to learn more about the concept of color mixing and find out some really interesting answers to common questions about it.
Why Green and Blue?
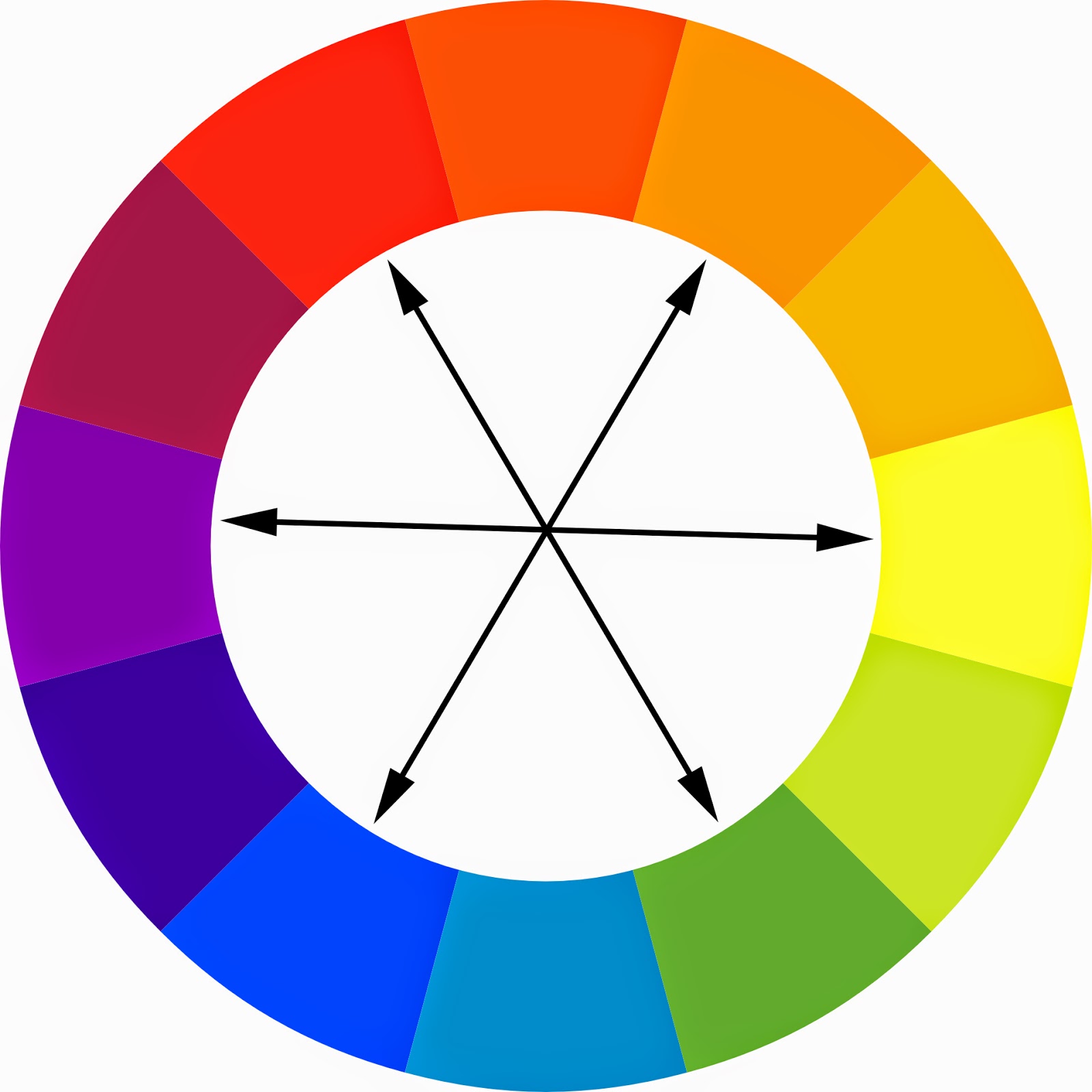
Green and blue are, you know, neighbors on the color wheel, and they share some visual characteristics. This closeness makes their combination particularly interesting because they can blend into a range of similar, yet distinct, shades. It’s not like mixing, say, red and green, which tend to make brown or yellow, which are quite different. With green and blue, the results often feel like a natural progression, which is quite cool.
Green and Blue in Light: Additive Mixing
When you put together green and blue lights, a really interesting thing happens, you know. It's not like mixing paints at all. When green and blue mix in lights, the result is cyan. This is what we call additive color mixing, where light waves combine to create new colors. It's how your TV or computer screen works, with tiny red, green, and blue light dots making up all the pictures you see.
But why does this fascinating fusion happen? Well, basically, light colors work by adding wavelengths together. When the wavelengths of green light and blue light overlap, their combined energy creates the perception of cyan. This process is, you know, fundamentally different from what happens when you mix physical pigments, and it’s a core principle in digital displays and stage lighting. It’s quite amazing how light behaves this way, truly.
Understanding Cyan
Cyan is a bright, clear blue-green color, and it’s one of the primary colors in the CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black) color model used in printing. So, it's very important for anyone who prints things. In the world of light, cyan is a secondary color, meaning it's created by mixing two primary light colors, in this case, green and blue. It’s a color that often feels fresh and modern, and you see it a lot in digital designs, which is pretty neat.
Green and Blue with Pigments: Subtractive Mixing
Now, when you talk about mixing green and blue with paints or pigments, that's a whole different story, you know. This is called subtractive color mixing, where pigments absorb certain wavelengths of light and reflect others. When you mix blue and green, you can end up with turquoise. This is because the pigments are taking away certain colors from the light spectrum, and what’s left for our eyes to see is the resulting shade.
The outcome, you know, can vary quite a bit depending on the specific shades of green and blue you start with. A very deep blue mixed with a bright green might give you a darker turquoise, while lighter shades could produce something more like a seafoam green. It's all about how those tiny pigment particles interact and absorb light, so it’s pretty complex in a way.
Exploring Turquoise
Turquoise is a beautiful color, a blue-green that reminds many people of tropical waters or precious gemstones. It's often described as a mix of blue and green, and that’s exactly what it is when you combine pigments. The specific hue will depend on the ratio of blue to green, meaning if you use more blue paint, it will lean more towards blue, and if you use more green, it will lean more towards green. It’s a very versatile color, really.
The Ratio Matters
As we touched on, the specific hue you get when mixing green and blue, it's almost entirely dependent on the ratio of blue to green you use. If you add just a little bit of blue to a lot of green, you'll get a greenish-turquoise, or perhaps a deep teal. On the other hand, if you add a lot of blue to a little green, you might end up with a more bluish-turquoise, or even an aqua shade. Experimenting with different amounts is, you know, the best way to find the exact shade you’re looking for. This is where the art truly comes in, you know.
The Bigger Picture: Color Theory and Perception
Understanding what color green and blue make is, in a way, just one piece of a much larger puzzle called color theory. Color theory is the art and science of using color. It’s a field that explains how humans perceive color, both physically and psychologically, and how colors mix, match, and contrast with each other. This knowledge is, basically, vital for anyone who works with visuals, from graphic designers to interior decorators.
The meaning of color is a phenomenon of light, or visual perception, that enables one to differentiate otherwise identical objects. It's not just about what colors look good together, but also about how colors make us feel and what messages they convey. So, learning about color theory is, in fact, a very important step for anyone wanting to truly master visual communication. It's quite a deep subject, really.
How We See Color
Our eyes are, you know, pretty amazing tools. They have special cells called cones that are sensitive to different wavelengths of light – primarily red, green, and blue. When light hits an object, some wavelengths are absorbed, and others are reflected. The reflected wavelengths are what our eyes pick up, and our brains then interpret these signals as specific colors. So, when you mix green and blue, your eyes are simply receiving a new combination of light signals, which your brain then translates into a new color, perhaps turquoise or cyan, depending on the source. It’s a complex process, you know, but truly fascinating.
The Science Behind the Art
Color theory, it's interesting, bridges the gap between science and art. It takes the physical properties of light and pigments and applies them to artistic and design principles. For instance, knowing that green and blue light create cyan is a scientific fact, but using that cyan effectively in a digital artwork is an art. Similarly, understanding how different ratios of blue and green paint create various shades of turquoise is scientific, yet choosing the perfect turquoise for a painting is an artistic choice. It’s a blend of logic and creativity, you know, which makes it so compelling.
Digital Colors: HTML and Beyond
In the digital world, colors are represented in a very precise way, you know. A HTML color code is an identifier used to represent a color on the web and within other digital assets. Common color codes are in the forms of a keyword name, a hexadecimal value, or an RGB value. These codes allow designers and developers to ensure that colors appear consistently across different screens and devices, which is pretty important for a good user experience.
For instance, an RGB value like `rgb(0, 255, 0)` represents pure green, and `rgb(0, 0, 255)` represents pure blue. When you mix these digitally, you're essentially adding the light values together, similar to how stage lights work. You can explore flat design colors, Google Material Design, Fluent colors, and Metro design schemes, all with hex and RGB color codes. These are, basically, widely used standards for web design, so it's quite relevant.
Decoding HTML Color Codes
HTML color codes are, in some respects, like secret languages for colors. A hexadecimal value, for example, is a six-digit code preceded by a hash symbol (#), where each pair of digits represents the amount of red, green, and blue light. So, you know, `#00FF00` is pure green, and `#0000FF` is pure blue. When you combine them digitally, you're looking at a different kind of mix than with paint. They are divided by color categories and listed alphabetically for quick navigation on many color resource sites. It's a very systematic way to handle color, actually.
Millions of Hues
It's quite amazing to think about how many colors are possible in the digital space, you know. We have 256 possible red shades, 256 possible green shades, and 256 possible blue shades. When you multiply these possibilities together, that's 256 x 256 x 256, which equals a staggering 16,777,216 colors! This vast number means that virtually any shade you can imagine, including all the subtle variations of blue-green, can be accurately represented on a screen. This capability is, you know, a huge part of why digital art and design are so rich and detailed. It truly offers a massive palette for creators.
Tools to Help You Mix and Match
For artists, students, and designers who want to explore color mixing further, there are many helpful tools available, you know. You can try our interactive color combination tool, for instance, which can help you see how different colors blend. These tools are often designed to make understanding color relationships much easier, which is pretty handy. They can help you create the perfect palette or get inspired by thousands of beautiful color schemes.
Some tools allow you to create, browse, and save palettes on the go, making it super convenient to work on your color ideas whenever inspiration strikes. Want to know what colors look good together? Canva's color wheel makes color combinations easy, for example. It's a great way to visually understand how colors interact and complement each other, which is, you know, a big part of successful design.
Interactive Color Tools
There are many interactive tools out there that let you play around with color, you know, virtually mixing them without making a mess. For instance, Colorhexa.com is a free color tool providing information about any color and generating matching color palettes for your designs, such as complementary, analogous, triadic, or tetradic. You can browse palettes, colors, schemes, and much more, including name, hex, RGB, HSL, HSV, CMYK, YCbCr, X11, Pantone, and RAL values. These tools are, basically, invaluable for exploring the vast world of color and seeing how different combinations truly work.
These kinds of designer tools are, in a way, like having a personal color expert at your fingertips. They help you create color combinations that work together well. Formerly known as color scheme designer, many of these platforms have evolved to offer even more features. You can use the color wheel to create great color palettes, seeing how green and blue, and their resulting shades, fit into a larger scheme. It’s a very practical way to learn, really.
Finding Perfect Palettes
Beyond just mixing two colors, these tools can also help you build entire color palettes. This is where you combine several colors that look good together, creating a harmonious or striking visual effect. For instance, once you understand the range of turquoises you can get from mixing green and blue, you can then find other colors that complement those shades. You can check out our color chart page to get inspired, which is a great starting point for finding new ideas. It's all about making informed choices for your designs, you know, and these tools really help with that.
Frequently Asked Questions About Green and Blue Mixing
What happens when you mix green and blue?
When you mix green and blue, what color do you get? Well, it really depends on whether you're talking about light or physical pigments. If you're mixing light, like on a screen, you'll get cyan. If you're mixing paints or other pigments, you can end up with turquoise. The specific shade of turquoise, you know, will vary quite a bit depending on the exact ratio of green to blue that you use, and also the particular shades of green and blue you start with. It's quite interesting how those two different outcomes happen, really.
What color does blue and green make in paint?
When you combine blue and green paint, you typically get a range of colors that fall into the blue-green spectrum, with turquoise being the most common result. The exact shade, you know, can lean more towards blue or more towards green, depending on how much of each color you add. For example, a little more blue might give you a deeper, richer turquoise, while a little more green could result in a brighter, more vibrant aqua. It's all about experimentation to find the shade you want, which is pretty fun.
What color does blue and green make in light?
When blue light and green light are mixed together, they produce cyan. This is a principle of additive color mixing, which is how colors are created on digital displays, such as your computer monitor or television screen. Unlike mixing paints, where colors absorb light, mixing light colors involves adding their wavelengths together. So, the combined wavelengths of blue and green light create the distinct color of cyan, which is, you know, quite a bright and clear shade. This is a very fundamental concept in how we see digital images, actually.
So, whether you're working with lights or paints, understanding what color green and blue make is, you know, a great step in mastering color. The specific hue will depend on the ratio of blue to green, and the medium you're using. You can learn more about color theory and perception on our site, which is really helpful for anyone interested in visuals. It's a journey of discovery, really, and there's always more to learn about how colors interact. It's been a passion since 2002, and we love sharing what we know.


Detail Author:
- Name : Prof. Lynn Bode II
- Username : nola58
- Email : murphy.emily@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1989-07-11
- Address : 84346 Ullrich Mills Felicialand, CA 93299-8267
- Phone : +1-667-967-2956
- Company : Cassin-Kuhn
- Job : Semiconductor Processor
- Bio : Voluptatem fugiat nesciunt quos consequatur ea tempore. Veritatis quis dolorum porro ut aut et. Aperiam corporis nulla dolor delectus voluptatibus. Ea aspernatur qui autem corporis pariatur rerum.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/ebertg
- username : ebertg
- bio : Ea ut rerum aliquid dolor.
- followers : 6377
- following : 364
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/gerhard9325
- username : gerhard9325
- bio : Aliquid nam repellat perferendis. Ipsam quia autem eos sit. Numquam ullam qui et delectus nesciunt.
- followers : 4723
- following : 614
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@gerhard_ebert
- username : gerhard_ebert
- bio : Culpa sapiente ullam qui quia qui pariatur rerum.
- followers : 1186
- following : 2201
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/ebert1988
- username : ebert1988
- bio : Enim nihil corrupti quae quis inventore aliquam. Aut laborum sed adipisci.
- followers : 591
- following : 1300
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/gerhard7471
- username : gerhard7471
- bio : Perspiciatis minima eligendi nihil commodi. Magnam totam voluptate dolores eos in molestias nihil. Quaerat ad id laudantium recusandae dolor odio voluptatem.
- followers : 6374
- following : 255

